
When studying people in a family, a pedigree depicting the phenotypes of two to three generations can be used to extrapolate the unknown genotypes. Since homozygous dominant and heterozygous display the same phenotype, 75 percent of the F2 generation will express the dominant – or wild type – trait, and 25 percent will express the recessive trait the ratio is 3:1. If two of those heterozygous individuals are mated, 25 percent of the resulting F2 generation will be homozygous dominant, 50 percent will be heterozygous, and 25 percent will be homozygous recessive the ratio is 1:2:1. The recessive trait needs another carrier and a bit of luck to be seen. In a simple cross between a homozygous dominant parent and a homozygous recessive parent, all the F1 offspring will be heterozygous – each will have one dominant and one recessive copy of the gene – and the phenotype will be the dominant trait. Recessive traits like red hair can skip generations because they can hide out in a carrier behind a dominant trait. The first generation of offspring is called F1, and the next generation is F2, etc. Punnet squares are graphs representing the genotypes that would hypothetically result from a cross of parents of known genotype. On the other hand, a recessive trait only affects an individual if he has two identical – homozygous – copies of that gene. In most sexually reproducing organisms, each individual has two alleles for each gene (one from each parent). Recessive alleles are only expressed when no dominant allele is present. A dominant trait is expressed (phenotype) whenever that allele is present, whether homozygous or heterozygous (genotype). Genes come in different versions, or alleles, with dominant alleles being expressed over recessive alleles. The combination of genes results in the phenotype, the actual observable trait. Homozygous and heterozygous describe the genotype. An individual is homozygous for a particular gene if he has two identical versions of that gene whereas, he is heterozygous if he has two different versions of that gene. The color of a person’s eyes will depend. In humans, eye color depends on several genes, each of which has several alleles. An example of this is found in the color of the eyes.
#What is recessive and dominant traits full
To get the full list of dominant/recessive traits, check out the video below and see for yourself what kind of genes you carry.Mendelian traits – the characteristics studied by Gregor Mendel – are determined by a single gene. A gene can have several alternative forms (called alleles), each with a different DNA sequence and expressing the same trait differently. Other more obscure dominant traits are the ability to roll your tongue and a tendency to cross your left thumb over your right when folding your hands. The ability to sing well is recessive so you may be able to pass it on to your children even if you can't hold a note yourself. If you happen to be a hairy person, you can guarantee that your children will also inherit this particularly fuzzy trait because it’s caused by a dominant gene. For example, the gene for having an extra finger is actually dominant, while the gene for having a tall stature is a recessive trait. For the most part, however, these traits make no difference other than changing how an individual looks.īuzzfeed recently created video urging viewers to guess which traits are dominant and which are recessive and have overturned the common misconception that dominant traits are always the most common traits. In autosomal recessive inheritance, a genetic condition occurs when one variant is.
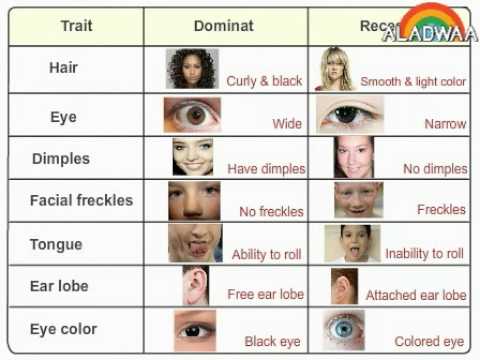
Traits such as albinism, hemophilia, deafness, and poor eyesight are all less desirable recessive traits. Compare dominant and recessive genes and traits and observe them in humans. One of the ways a genetic trait or a genetic condition can be inherited. For example, traits such as immunity to poison ivy, normal eyesight and hearing, and normal blood clotting abilities are all expressions of dominant genes.

When combined together in an offspring, the dominant trait will always be expressed over the recessive trait. Dominant allele: The trait that has a higher probability of occurring and more likely to been. There are two types of genetic traits: dominant and recessive. Dominant alleles will almost always mask recessive alleles. Directions: Check off in the table below whether you inherited the dominant (D) or recessive (R) gene for the following genetic traits. They are responsible for everything, from your curly or straight hair to whether or not you will develop certain health conditions later in life. Genes are the tiny pieces of molecular information that determine who we are.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
